How 5G and Beyond Are Transforming Our Connected World

The telecommunications industry stands at the forefront of technological innovation, continuously reshaping how we communicate, work, and live. From the early days of telegraph systems to today’s ultra-fast 5G networks, telecom has been the backbone of global connectivity. In this post, we’ll explore the current state of telecommunications and what the future holds for this dynamic industry.
The 5G Revolution: More Than Just Speed

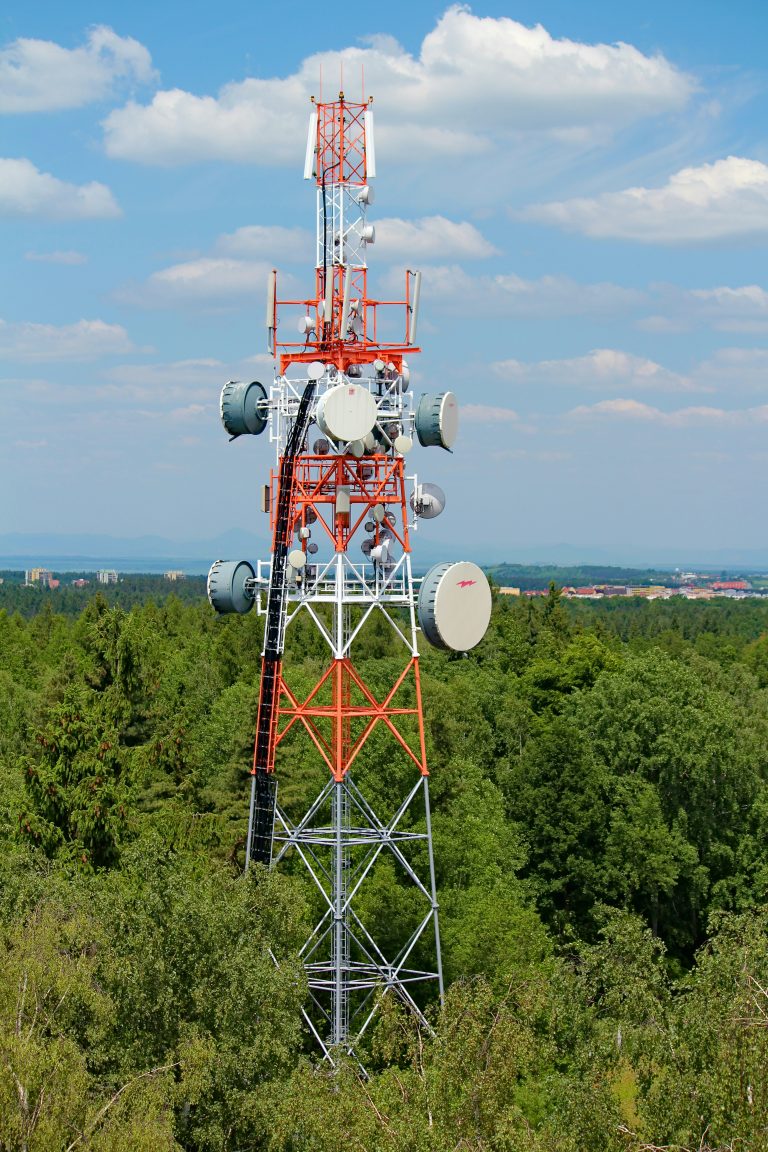
Fifth-generation wireless technology (5G) represents a quantum leap in mobile connectivity. While most people associate 5G with faster download speeds, its impact extends far beyond streaming videos more quickly.
Key Benefits of 5G Technology:
Ultra-Low Latency: 5G networks can achieve latency as low as 1 millisecond, making real-time applications like remote surgery and autonomous vehicles possible.
Massive Device Connectivity: 5G can support up to 1 million devices per square kilometer, essential for the expanding Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
Enhanced Reliability: Network slicing allows telecom operators to create virtual networks tailored to specific use cases, ensuring consistent performance for critical applications.
Energy Efficiency: Despite higher speeds, 5G technology is designed to be more energy-efficient per bit of data transmitted compared to 4G.
The Rise of Edge Computing in Telecom

Edge computing is revolutionizing how telecom networks process data. By moving computation closer to data sources, edge computing reduces latency and bandwidth usage while improving response times.
Telecom companies are deploying edge data centers at cell tower locations, enabling applications that require immediate processing, such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and real-time analytics. This distributed architecture is crucial for supporting the massive data flows generated by 5G networks and IoT devices.
IoT and Smart Cities: Telecom’s Role in Urban Transformation

Telecommunications infrastructure forms the nervous system of smart cities. As urban areas become more connected, telecom networks enable:
- Smart Traffic Management: Real-time traffic monitoring and adaptive signal control reduce congestion and emissions
- Public Safety Systems: Integrated surveillance and emergency response networks improve security
- Utility Management: Smart grids and water systems optimize resource consumption
- Environmental Monitoring: Sensor networks track air quality, noise levels, and weather conditions
The deployment of 5G networks accelerates smart city development by providing the bandwidth and reliability needed for millions of connected devices to operate simultaneously.
Cybersecurity Challenges in Modern Telecom

As telecom networks become more complex and interconnected, cybersecurity has emerged as a critical concern. The industry faces several challenges:
Network Vulnerabilities: The transition to software-defined networks and virtualized infrastructure creates new attack surfaces that must be protected.
IoT Device Security: Billions of connected devices often lack robust security features, making them potential entry points for cyberattacks.
Data Privacy: With networks carrying sensitive personal and business data, telecom companies must implement stringent privacy protections to comply with regulations like GDPR and maintain customer trust.
Leading telecom operators are investing heavily in AI-powered security systems that can detect and respond to threats in real-time, ensuring network integrity and customer data protection.
The Path to 6G: What’s Next?

While 5G deployment continues worldwide, researchers are already developing sixth-generation (6G) wireless technology. Expected to launch commercially around 2030, 6G promises:
- Terahertz frequencies: Enabling speeds up to 100 times faster than 5G
- AI-native networks: Deep integration of artificial intelligence into network operations
- Holographic communications: Supporting truly immersive telepresence experiences
- Sensing capabilities: Networks that can detect environmental conditions and object locations
6G will likely integrate terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks, incorporating satellites and high-altitude platforms to ensure truly global coverage.
Sustainability in Telecommunications
The telecom industry is increasingly focused on environmental sustainability. Network infrastructure consumes significant energy, and companies are taking steps to reduce their carbon footprint:
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources for data centers and cell towers
- Implementing energy-efficient equipment and cooling systems
- Optimizing network traffic to reduce unnecessary energy consumption
- Promoting device recycling and circular economy initiatives
Major telecom operators have committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2040 or earlier, recognizing their responsibility in addressing climate change.
Conclusion: Staying Connected in an Evolving Landscape
The telecommunications industry continues to evolve at a breathtaking pace, driven by technological innovation and changing consumer demands. From 5G networks enabling new applications to the promise of 6G on the horizon, telecom remains central to our increasingly digital lives.
As we look to the future, the successful telecom companies will be those that balance innovation with security, performance with sustainability, and global reach with local relevance. The connected world of tomorrow is being built today, one cell tower, fiber optic cable, and software update at a time.