Introduction
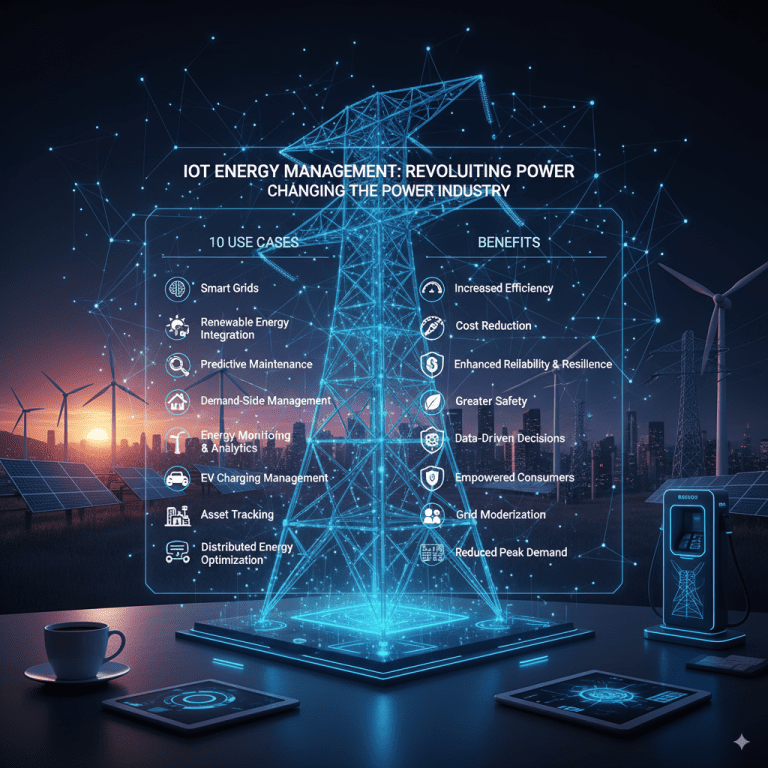
The adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) technology is revolutionizing energy management across industries. By enabling real-time monitoring, automation, and data-driven optimization, IoT solutions help reduce costs, increase efficiency, and support sustainability goals. In the dynamically evolving power industry, IoT is a game-changer, transforming how energy is generated, distributed, and consumed.
Here are 10 impactful IoT use cases in energy management and the benefits that are reshaping the power landscape in 2025.
1. Smart Commercial Buildings
IoT devices optimize lighting, HVAC systems, and energy consumption based on occupancy and time of day. Automated control reduces unnecessary energy use and cuts costs in offices, warehouses, and retail spaces.
2. Smart Metering and Real-Time Energy Monitoring
IoT-enabled smart meters provide granular usage data for consumers and utilities. This helps track energy consumption patterns, detect inefficiencies, and optimize demand response strategies.
3. Predictive Maintenance for Energy Assets
IoT sensors monitor equipment health indicators such as temperature and vibration to anticipate failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
4. Automated Energy Optimization
By analyzing real-time data on environmental conditions and usage, IoT systems can dynamically adjust energy consumption, such as dimming lights or modulating HVAC, resulting in efficient resource use.
5. Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
IoT manages and monitors solar panels, wind turbines, and other green energy assets. It enables smarter distribution, load balancing, and storage, supporting grid stability and sustainability.
6. Demand Response Management
Utilities leverage IoT data to adjust supply dynamically in response to consumer demand spikes, minimizing blackouts and optimizing grid performance.
7. Energy Theft and Fault Detection
IoT sensors detect anomalies indicating theft or faults in the grid infrastructure, improving security and reducing revenue losses.
8. Grid Automation and Remote Control
IoT-enabled automation allows utilities to remotely monitor and manage substations, transformers, and distribution networks, improving reliability and reducing operating costs.
9. Asset Lifecycle Management
IoT tracks energy infrastructure usage metrics and conditions to optimize replacements, upgrades, and budgeting, extending asset life and enhancing ROI.
10. Enhanced Consumer Engagement
Consumers receive actionable insights through IoT-powered apps and devices, promoting energy-saving behaviors and enabling participation in energy markets (e.g., trading surplus solar energy).
Benefits
-
Cost Savings: Reduced energy waste cuts operational expenses.
-
Energy Efficiency: Optimized consumption and supply balancing enhance system performance.
-
Sustainability: Supports green energy adoption and reduces carbon footprint.
-
Operational Transparency: Real-time data improves decision-making and regulatory compliance.
-
Improved Reliability: Predictive maintenance and fault detection minimize outages.
-
User Empowerment: Engages consumers in managing their energy usage actively.
Conclusion
IoT energy management is a cornerstone of the future power industry—creating smarter, cleaner, and more resilient energy ecosystems. Businesses, utilities, and consumers alike stand to benefit from adopting connected energy solutions and leveraging data-driven insights.
For expert guidance on integrating IoT and AI into energy management, explore TechOTD AI Services and stay updated with innovations on the TechOTD Blog.
Would you like a detailed technical overview or case studies illustrating IoT impact in energy?# 10 Use Cases and Benefits of IoT Energy Management Changing the Power Industry
Introduction
The adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) technology is revolutionizing energy management across industries. By enabling real-time monitoring, automation, and data-driven optimization, IoT solutions help reduce costs, increase efficiency, and support sustainability goals. In the dynamically evolving power industry, IoT is a game-changer, transforming how energy is generated, distributed, and consumed.
Here are 10 impactful IoT use cases in energy management and the benefits that are reshaping the power landscape in 2025.
1. Smart Commercial Buildings
IoT devices optimize lighting, HVAC systems, and energy consumption based on occupancy and time of day. Automated control reduces unnecessary energy use and cuts costs in offices, warehouses, and retail spaces.
2. Smart Metering and Real-Time Energy Monitoring
IoT-enabled smart meters provide granular usage data for consumers and utilities. This helps track energy consumption patterns, detect inefficiencies, and optimize demand response strategies.
3. Predictive Maintenance for Energy Assets
IoT sensors monitor equipment health indicators such as temperature and vibration to anticipate failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
4. Automated Energy Optimization
By analyzing real-time data on environmental conditions and usage, IoT systems can dynamically adjust energy consumption, such as dimming lights or modulating HVAC, resulting in efficient resource use.
5. Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
IoT manages and monitors solar panels, wind turbines, and other green energy assets. It enables smarter distribution, load balancing, and storage, supporting grid stability and sustainability.
6. Demand Response Management
Utilities leverage IoT data to adjust supply dynamically in response to consumer demand spikes, minimizing blackouts and optimizing grid performance.
7. Energy Theft and Fault Detection
IoT sensors detect anomalies indicating theft or faults in the grid infrastructure, improving security and reducing revenue losses.
8. Grid Automation and Remote Control
IoT-enabled automation allows utilities to remotely monitor and manage substations, transformers, and distribution networks, improving reliability and reducing operating costs.
9. Asset Lifecycle Management
IoT tracks energy infrastructure usage metrics and conditions to optimize replacements, upgrades, and budgeting, extending asset life and enhancing ROI.
10. Enhanced Consumer Engagement
Consumers receive actionable insights through IoT-powered apps and devices, promoting energy-saving behaviors and enabling participation in energy markets (e.g., trading surplus solar energy).
Benefits
-
Cost Savings: Reduced energy waste cuts operational expenses.
-
Energy Efficiency: Optimized consumption and supply balancing enhance system performance.
-
Sustainability: Supports green energy adoption and reduces carbon footprint.
-
Operational Transparency: Real-time data improves decision-making and regulatory compliance.
-
Improved Reliability: Predictive maintenance and fault detection minimize outages.
-
User Empowerment: Engages consumers in managing their energy usage actively.
>
Conclusion
IoT energy management is a cornerstone of the future power industry—creating smarter, cleaner, and more resilient energy ecosystems. Businesses, utilities, and consumers alike stand to benefit from adopting connected energy solutions and leveraging data-driven insights.
For expert guidance on integrating IoT and AI into energy management, explore TechOTD AI Services and stay updated with innovations on the TechOTD Blog.