Introduction
In the fast-paced world of software development, agility and reliability are critical for success. As businesses race to deliver software faster without compromising quality, a modern methodology called DevOps has become the cornerstone of innovation.
DevOps combines “Development” and “Operations” — breaking the traditional silos between software engineers and IT teams. This collaboration allows organizations to deliver updates quickly, respond to user needs faster, and maintain high performance across systems.
But what exactly is DevOps, and why has it become essential in 2025? Let’s explore.
What Is DevOps?
DevOps is a cultural and technical approach that unites software development and IT operations to achieve continuous integration, delivery, and improvement. The goal is simple: shorten the software development lifecycle while maintaining quality and stability.
Instead of working separately, developers, testers, and system administrators collaborate using automation tools, shared metrics, and continuous feedback loops. This promotes faster releases, fewer bugs, and better customer satisfaction.
In short, DevOps isn’t just about tools—it’s about teamwork, automation, and a culture of continuous improvement.
The Core Principles of DevOps
DevOps is built on a few key principles that guide how teams work together:
-
Collaboration and Communication – DevOps breaks down barriers between developers and operations teams, promoting transparency and shared responsibility.
-
Automation – From testing to deployment, automation reduces manual errors and speeds up delivery.
-
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) – Regularly merging and deploying code ensures faster releases and immediate bug detection.
-
Monitoring and Feedback – Constant monitoring allows teams to detect issues early and improve system performance.
-
Security Integration (DevSecOps) – Security is embedded into every stage of development rather than being added at the end.
These principles enable organizations to innovate faster while maintaining system reliability and security.
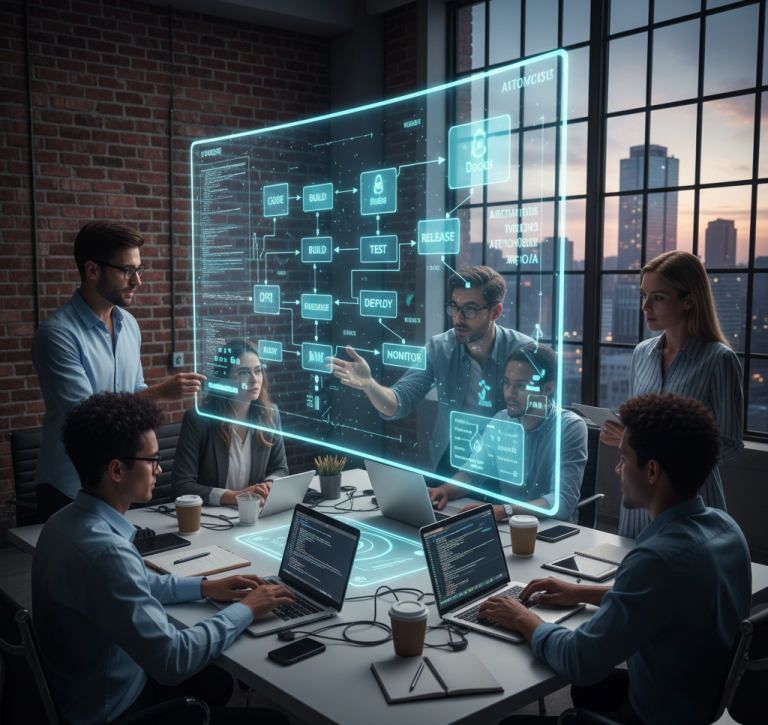
The DevOps Lifecycle
The DevOps lifecycle represents the continuous loop of development, integration, deployment, and monitoring. It typically includes the following stages:
-
Plan – Teams collaborate to define requirements and goals.
-
Code – Developers write and review code collaboratively.
-
Build – Code is compiled, tested, and packaged for deployment.
-
Test – Automated testing ensures code quality and reliability.
-
Release – Approved builds are deployed to production environments.
-
Deploy – Software is automatically deployed using pipelines.
-
Operate – Systems are monitored for performance and availability.
-
Monitor – Real-time feedback is collected for continuous improvement.
This cyclical process ensures faster delivery and consistent software quality.
Benefits of Adopting DevOps
Implementing DevOps brings a wide range of business and technical advantages:
-
Faster Software Delivery – Automated workflows and CI/CD pipelines speed up deployment cycles.
-
Improved Collaboration – Cross-functional teams communicate better, reducing bottlenecks.
-
Higher Quality Software – Continuous testing ensures fewer bugs and more stable releases.
-
Greater Customer Satisfaction – Quick updates and reliable performance improve user experience.
-
Increased Efficiency – Automation reduces repetitive manual tasks.
-
Scalability – DevOps practices enable businesses to scale applications quickly as demand grows.
For modern organizations, these benefits translate into innovation, cost efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Common DevOps Tools
DevOps thrives on the right set of tools that support integration, automation, and monitoring. Some of the most popular tools include:
-
Jenkins – Automates CI/CD pipelines.
-
Docker – Simplifies containerization and application deployment.
-
Kubernetes – Manages container orchestration.
-
Git & GitHub – Enables version control and team collaboration.
-
Ansible & Puppet – Automate infrastructure configuration.
-
Prometheus & Grafana – Provide system monitoring and alerting.
These tools empower teams to build, test, and deploy faster while maintaining reliability and visibility.
DevOps in 2025: Emerging Trends
As technology evolves, DevOps continues to adapt. Here are the top trends shaping DevOps in 2025:
-
AI-Driven DevOps (AIOps) – Artificial intelligence helps automate decision-making, detect anomalies, and predict failures.
-
GitOps – Managing infrastructure through Git repositories for versioned and auditable automation.
-
Serverless Architectures – Enabling faster, cost-effective deployment without server management.
-
DevSecOps Expansion – Integrating security into every step of development.
-
Cloud-Native Development – Leveraging multi-cloud strategies for scalability and flexibility.
These trends are transforming DevOps into a more intelligent, automated, and secure approach to software delivery.
Challenges in Implementing DevOps
While DevOps offers immense benefits, implementation isn’t without challenges:
-
Cultural Resistance – Teams may struggle to adapt to new collaborative models.
-
Tool Overload – Choosing and managing too many tools can cause confusion.
-
Skill Gaps – DevOps requires multidisciplinary expertise.
-
Security Concerns – Faster deployments can introduce vulnerabilities if not managed properly.
Organizations overcome these challenges through training, leadership support, and adopting DevOps gradually across teams.
Conclusion
DevOps is more than just a buzzword—it’s a fundamental shift in how software is built and delivered. By merging development, operations, and automation, organizations achieve agility, reliability, and continuous innovation.
In 2025 and beyond, DevOps remains the foundation of digital success. Businesses that embrace it gain the agility to deliver faster, adapt to market changes, and meet customer expectations effortlessly.
Whether you’re a startup or an enterprise, adopting DevOps today ensures you’re prepared for the digital challenges of tomorrow.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of DevOps?
To improve collaboration between development and operations teams and speed up software delivery cycles.
2. What are the key stages of the DevOps lifecycle?
Planning, coding, building, testing, releasing, deploying, operating, and monitoring.
3. How does DevOps improve efficiency?
Automation and CI/CD pipelines reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and accelerate deployments.
4. What is the difference between Agile and DevOps?
Agile focuses on iterative software development, while DevOps extends it to include deployment and operations.
5. What are common DevOps tools?
Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, Git, Ansible, and Prometheus.
6. Is DevOps relevant for non-tech companies?
Yes, any organization that develops or uses software can benefit from DevOps to improve delivery and performance.