Introduction
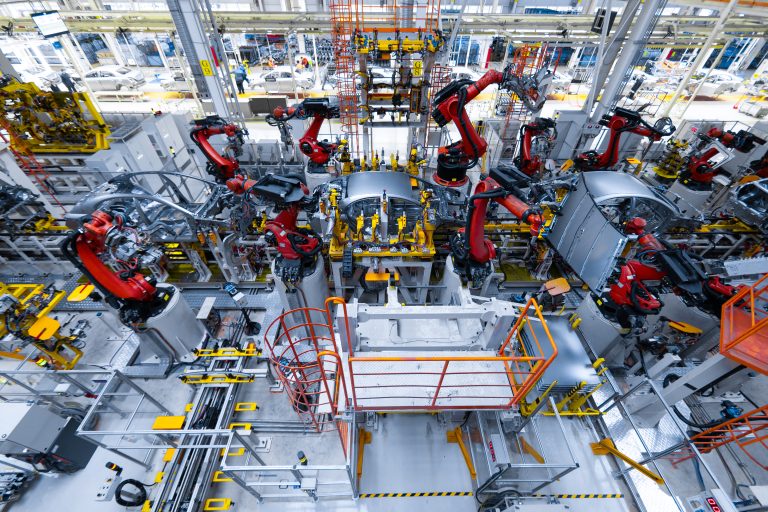
Manufacturing has always been the backbone of economic development. From handcrafting tools in ancient times to modern automated factories, manufacturing defines progress. Today, this sector is undergoing a massive transformation powered by technology, sustainability, and global connectivity.
The Evolution of Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry has come a long way since the Industrial Revolution.
-
1st Industrial Revolution (18th century): Introduction of steam engines and mechanization.
-
2nd Industrial Revolution: Rise of electricity, mass production, and assembly lines.
-
3rd Industrial Revolution: Use of computers and automation.
-
4th Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0): Smart factories powered by AI, IoT, robotics, and data analytics.
Each stage brought efficiency, innovation, and new opportunities for industries and workers alike.
Modern Manufacturing: Technology at Work
Today’s factories are smarter and faster than ever before.
Here are some key technologies driving change:
-
Automation and Robotics: Machines now handle repetitive tasks with precision and speed.
-
3D Printing: Enables custom, small-batch production at low cost.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Predicts demand, reduces waste, and optimizes processes.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): Connects machines and sensors for real-time monitoring.
-
Big Data & Analytics: Improves quality control and decision-making.
Sustainability in Manufacturing
Modern manufacturing focuses not just on profit but also on the planet.
Companies are adopting eco-friendly materials, recycling systems, and energy-efficient technologies. Green manufacturing aims to minimize waste and reduce carbon footprints while maintaining high productivity.
Challenges in the Manufacturing Industry
Despite the progress, the sector faces several challenges:
-
Shortage of skilled labor
-
High initial investment for automation
-
Supply chain disruptions (e.g., global pandemics)
-
Adapting to environmental regulations
Overcoming these challenges requires innovation, upskilling workers, and government support for technology-driven initiatives.
The Future of Manufacturing
The future lies in smart manufacturing — a combination of human creativity and digital intelligence.
We can expect:
-
Fully connected “smart factories”
-
Increased use of renewable energy
-
AI-driven predictive maintenance
-
Global collaboration between machines and humans
This future will be faster, cleaner, and more efficient, driving growth across economies.
Conclusion
Manufacturing is entering a new era of intelligence and sustainability. With advancements in automation, AI, and green innovation, the industry will continue to shape the way we live, work, and build. The future of manufacturing is not just about making products — it’s about making progress.