Introduction
The DevOps approach has become the foundation for modern software development. It’s not just a set of tools or techniques — it’s a continuous cycle of collaboration, automation, and delivery that bridges the gap between developers and operations teams.
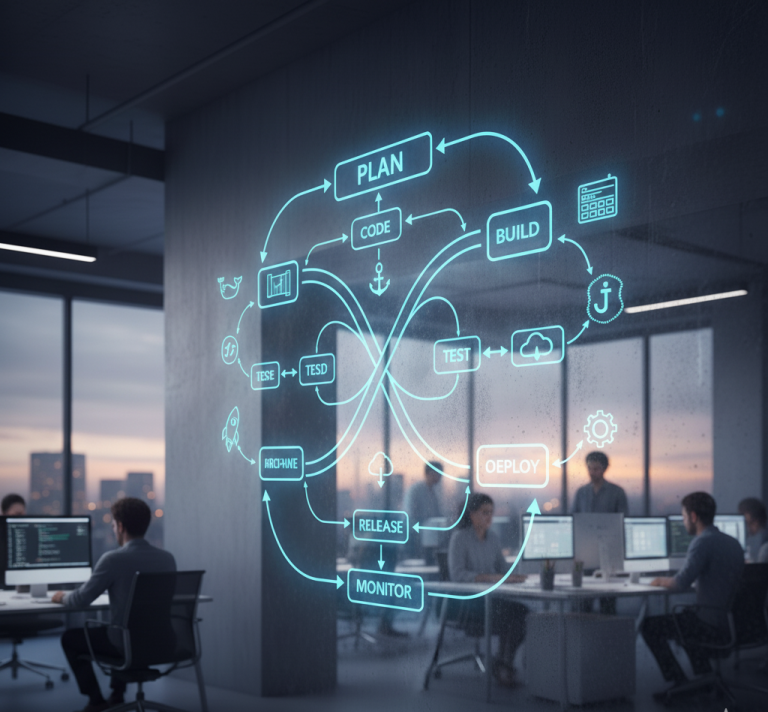
The DevOps lifecycle represents this entire journey — from writing code to deploying and maintaining applications in production. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring fast delivery, reliability, and continuous improvement.
Let’s dive into the complete DevOps lifecycle, its stages, benefits, and best practices every developer should know in 2025.
Understanding the DevOps Lifecycle
The DevOps lifecycle is a circular process that emphasizes continuous integration, testing, deployment, and feedback. Unlike traditional development, which follows a linear model, DevOps relies on continuous loops that allow teams to iterate quickly and adapt to change.
There are generally eight main stages in the DevOps lifecycle: plan, code, build, test, release, deploy, operate, and monitor. Together, these create a continuous feedback loop that drives innovation and efficiency.
1. Planning – Laying the Foundation
The first stage of the DevOps lifecycle begins with planning. Teams define goals, outline project scope, and determine the technical requirements for development and deployment.
Using tools like Jira, Trello, or Asana, developers and project managers collaborate to create a roadmap and assign responsibilities.
A well-structured plan sets the tone for smooth collaboration and ensures that both development and operations teams work toward the same objectives.
2. Coding – Building the Core
In the coding stage, developers start writing the application’s core functionality using programming languages and frameworks. Collaboration tools like Git and GitHub are used for version control, enabling developers to work together seamlessly on different parts of the codebase.
Following best coding practices, code reviews, and maintaining proper documentation are key to ensuring quality and maintainability.
This phase also emphasizes modularity and reusability, making it easier to integrate changes later.
3. Building – Continuous Integration Begins
Once the code is ready, it moves to the build stage, where it’s compiled and packaged for testing and deployment.
Using tools like Jenkins, Maven, or Gradle, teams automate the build process, ensuring faster delivery and error detection. Continuous Integration (CI) pipelines automatically merge and test new code to prevent conflicts.
This stage ensures that every code change integrates smoothly into the main application, maintaining system stability and consistency.
4. Testing – Ensuring Quality and Reliability
In this stage, testing is automated to validate the functionality, performance, and security of the code.
Tools such as Selenium, JUnit, or TestNG are used to run automated test scripts that check for bugs or performance issues. Continuous Testing ensures that every update or new feature meets quality standards before deployment.
The goal is to detect and fix issues early, reducing post-release problems and maintaining user satisfaction.
5. Release – Preparing for Deployment
Once the code passes testing, it moves to the release stage, where it’s prepared for deployment. Configuration management tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef help automate this process by defining environments and dependencies.
At this point, the team ensures version control and rollback mechanisms are in place, allowing safe and smooth transitions to production.
6. Deployment – Going Live
Deployment marks the transition from development to production. Using CI/CD pipelines (Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment), code is automatically deployed without human intervention.
Tools like Docker and Kubernetes make this process seamless by managing containers and orchestrating deployments across multiple environments.
This ensures faster releases and consistent delivery, regardless of the infrastructure.
7. Operation – Maintaining Stability
Once deployed, the application moves into the operation phase, where it is actively managed and maintained.
Operations teams ensure that the application is available, stable, and performing as expected. Tools like AWS CloudWatch, Nagios, or Datadog help monitor system resources and server health.
Any performance degradation or anomalies are addressed immediately to minimize downtime.
8. Monitoring – Continuous Feedback and Improvement
The final stage of the DevOps lifecycle focuses on monitoring performance, gathering user feedback, and identifying areas for improvement.
Monitoring tools such as Prometheus, Grafana, or Splunk help visualize real-time data, giving teams actionable insights into system behavior.
Continuous monitoring not only ensures reliability but also drives future innovation and system optimization.
Key Benefits of the DevOps Lifecycle
Implementing the DevOps lifecycle offers numerous advantages for organizations:
-
Faster Delivery: Automation and continuous integration accelerate software releases.
-
Improved Quality: Frequent testing ensures high-quality and bug-free releases.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Cross-functional teams work more efficiently together.
-
Reduced Downtime: Automated monitoring minimizes disruptions and improves reliability.
-
Scalability: DevOps supports dynamic scaling to handle changing workloads.
These benefits make DevOps indispensable for modern software development.
Best Practices for an Effective DevOps Lifecycle
To maximize the value of DevOps, organizations should follow these best practices:
-
Automate everything — from code integration to monitoring.
-
Foster open communication between development and operations.
-
Continuously measure performance using KPIs and metrics.
-
Integrate security at every stage (DevSecOps).
-
Encourage feedback loops for constant improvement.
Following these guidelines ensures a stable, efficient, and scalable DevOps workflow.
Conclusion
The DevOps lifecycle is a continuous loop that connects development, testing, deployment, and feedback in an agile and automated way. Each stage plays a critical role in delivering quality software faster and more reliably.
By adopting the DevOps lifecycle, organizations can bridge the gap between development and operations, reduce costs, and enhance innovation. In 2025 and beyond, companies that master these principles will stay ahead in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
FAQs
1. What is the DevOps lifecycle?
It’s a continuous process that includes planning, coding, building, testing, deploying, operating, and monitoring software applications.
2. Why is the DevOps lifecycle important?
It enables faster, more reliable software delivery and promotes collaboration across teams.
3. What tools are used in the DevOps lifecycle?
Popular tools include Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, Ansible, Git, and Prometheus.
4. What is Continuous Integration in DevOps?
Continuous Integration automatically merges and tests code changes to detect issues early.
5. How does DevOps improve product quality?
Through automation and continuous feedback, it ensures consistent performance and reliability.
6. Is DevOps suitable for all industries?
Yes, any organization that relies on software development can benefit from DevOps principles.