Introduction
Building high-quality software requires more than just writing code. Successful applications are the result of a structured and disciplined approach that ensures efficiency, reliability, and scalability. This structured approach is known as the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC).
The SDLC defines a series of phases that guide software teams from the initial idea to final deployment and ongoing maintenance. By following a well-defined lifecycle, organizations can reduce risks, control costs, improve quality, and deliver software that meets user expectations.
In this blog, we will explore the software development lifecycle in detail, understand each phase, examine popular SDLC models, and learn why SDLC is essential for modern software development.
What Is the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC)?
The Software Development Lifecycle is a systematic process used to develop software applications. It outlines the steps required to design, build, test, deploy, and maintain software efficiently.
The main goals of SDLC are to:
-
Deliver high-quality software
-
Meet customer requirements
-
Reduce project risks
-
Ensure predictable timelines and budgets
SDLC provides a clear roadmap for developers, designers, testers, and stakeholders.
Why Is SDLC Important?
Following the SDLC helps organizations:
-
Improve project planning and management
-
Detect issues early in development
-
Enhance communication among teams
-
Deliver consistent and reliable software
Without a structured lifecycle, projects are more likely to face delays, budget overruns, and quality issues.
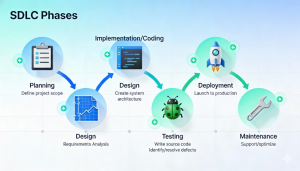
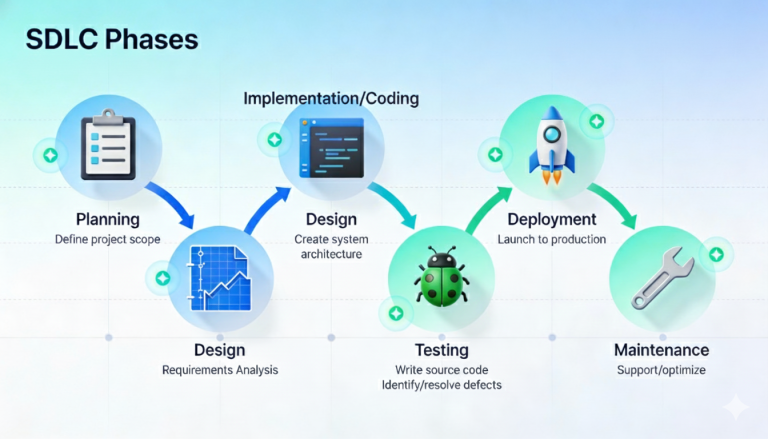
Phases of the Software Development Lifecycle
The SDLC typically consists of six to seven key phases.
1. Requirement Analysis
This is the foundation of the entire development process.
Key Activities
-
Gathering business requirements
-
Understanding user needs
-
Defining functional and non-functional requirements
-
Documenting requirements
Clear and accurate requirements prevent costly changes later in the project.
2. Planning
In the planning phase, teams define how the project will be executed.
Key Activities
-
Estimating timelines and costs
-
Allocating resources
-
Defining milestones and deliverables
-
Risk assessment
Effective planning ensures smooth project execution.
3. System Design
The design phase focuses on how the software will work.
Types of Design
-
High-Level Design (HLD): Overall architecture and system components
-
Low-Level Design (LLD): Detailed logic, data structures, and workflows
This phase translates requirements into a technical blueprint.
4. Development (Implementation)
This is where actual coding takes place.
Key Activities
-
Writing source code
-
Code reviews
-
Integrating components
Developers follow coding standards and best practices to ensure maintainability and performance.
5. Testing
Testing ensures the software works as intended.
Types of Testing
-
Unit testing
-
Integration testing
-
System testing
-
User acceptance testing (UAT)
Testing identifies bugs, security vulnerabilities, and performance issues before release.
6. Deployment
In this phase, the software is released to users.
Deployment Methods
-
Manual deployment
-
Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD)
Proper deployment strategies minimize downtime and risks.
7. Maintenance and Support
After deployment, the software enters the maintenance phase.
Key Activities
-
Bug fixes
-
Performance optimization
-
Feature enhancements
-
Security updates
Maintenance ensures long-term software reliability.
Popular SDLC Models
Different projects use different SDLC models based on requirements.
1. Waterfall Model
A linear and sequential approach suitable for projects with fixed requirements.
2. Agile Model
An iterative approach that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and continuous delivery.
3. Scrum
A popular Agile framework using short development cycles called sprints.
4. DevOps Model
Combines development and operations to enable faster and more reliable releases.
Choosing the Right SDLC Model
The right SDLC model depends on:
-
Project size and complexity
-
Requirement stability
-
Team structure
-
Timeline and budget
Choosing the correct model improves project outcomes.
SDLC in Modern Software Development
Modern development practices often blend SDLC with Agile and DevOps principles. Automation, cloud platforms, and continuous testing have transformed traditional lifecycle models into more flexible and efficient processes.
Conclusion
The Software Development Lifecycle is a critical framework that ensures software projects are delivered successfully. By understanding and following SDLC phases, organizations can build reliable, scalable, and secure applications.
Whether you are developing a small application or a large enterprise system, SDLC provides the structure needed to achieve consistent results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is SDLC in software development?
SDLC is a structured process that defines the stages involved in building, deploying, and maintaining software.
2. How many phases are in the SDLC?
Typically, SDLC consists of six to seven phases, including requirements, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
3. Which SDLC model is best?
There is no single best model. Agile is best for flexible projects, while Waterfall suits projects with fixed requirements.
4. Why is testing important in SDLC?
Testing ensures software quality, reliability, and security before release.
5. Can SDLC be combined with Agile?
Yes, modern development often integrates SDLC principles with Agile and DevOps practices.
6. Does SDLC apply to all software projects?
Yes, SDLC can be adapted to projects of all sizes and complexities.
Contact with us: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61555452386126