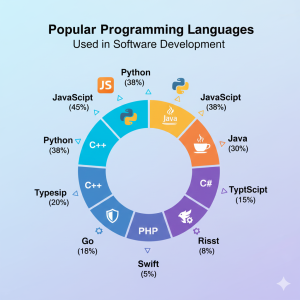
Introduction
In today’s digital-first world, mobile applications are no longer a luxury—they’re a necessity for businesses to connect with their customers. Choosing the right framework for mobile app development can determine the success of your app in terms of performance, scalability, and user experience. Among the many frameworks available, React Native has emerged as one of the most popular and powerful tools for building cross-platform apps with native-like performance.
This guide will take you through everything you need to know about React Native, from what it is and why it’s popular, to its benefits, use cases, challenges, and the future of the framework.
What is React Native?
React Native is an open-source mobile app development framework created by Meta (Facebook) in 2015. It allows developers to build cross-platform mobile apps using JavaScript and React, while rendering user interfaces with native components. This means that a single codebase can be used to build apps for both iOS and Android, significantly reducing development time and cost.
Why React Native is Popular
-
Cross-Platform Development – Write once, run on both iOS and Android.
-
Native Performance – Uses native components for smooth performance.
-
Strong Community Support – Backed by Meta and an active developer community.
-
Faster Time-to-Market – Saves time with reusable components and pre-built libraries.
-
Hot Reloading – Developers can instantly see the impact of code changes.
Key Features of React Native
-
Cross-Platform Compatibility
-
Hot Reloading and Fast Refresh
-
Third-Party Plugin Support
-
Large Ecosystem of Libraries
-
Reusable UI Components
-
Integration with Native Code (Java, Swift, Objective-C, Kotlin)
Benefits of Using React Native for Mobile App Development
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | One codebase for two platforms saves resources. |
| Faster Development | Shared code reduces development time. |
| Strong Community | Large developer community ensures constant updates and support. |
| Native Performance | Uses real native components for high performance. |
| Scalability | Suitable for small startups and large enterprises. |
| Easy Maintenance | Updates and bug fixes are easier with a shared codebase. |
Use Cases of React Native
React Native is versatile and is used by both startups and global enterprises. Some popular companies that use React Native include:
-
Facebook (Marketplace, Ads Manager)
-
Instagram
-
Uber Eats
-
Airbnb (initially)
-
Tesla
-
Walmart
-
Discord
Real-World Use Cases
-
E-Commerce Apps – Faster shopping experiences with cross-platform functionality.
-
On-Demand Delivery Apps – Food delivery, taxi booking apps benefit from native-like performance.
-
Social Media Apps – High responsiveness and seamless integration with device features.
-
Business Apps – Helps companies manage users and clients across platforms.
-
Educational Apps – Gamified learning platforms and video-based e-learning solutions.
React Native vs Other Frameworks
| Feature | React Native | Flutter | Xamarin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Language | JavaScript + React | Dart | C# |
| Performance | Near-native | High (Skia engine) | Moderate |
| Community | Very large | Growing fast | Limited |
| UI Flexibility | High | Very High | Moderate |
| Learning Curve | Easy for React devs | Moderate | Higher |
Challenges of React Native
-
Performance Gaps in highly complex apps.
-
Dependency on Third-Party Libraries (sometimes outdated).
-
Native Modules Required for advanced functionalities.
-
UI Consistency Issues between iOS and Android.
Best Practices for React Native Development
-
Use TypeScript for type safety.
-
Optimize Images and Assets for performance.
-
Break Components into Smaller Units for reusability.
-
Follow Modular Architecture to manage large projects.
-
Keep Dependencies Updated to avoid security risks.
Future of React Native
React Native continues to evolve with regular updates from Meta and the community. Upcoming improvements include:
-
Better performance with Hermes Engine (lightweight JavaScript engine).
-
New Architecture (Fabric, TurboModules, JSI) for faster rendering.
-
Integration with AI and Machine Learning SDKs.
-
Stronger community-driven ecosystem.
FAQs on React Native
Q1: Is React Native good for startups?
Yes, it reduces cost and time-to-market, making it ideal for startups.
Q2: Can React Native handle large-scale apps?
Yes, companies like Walmart and Tesla use it for enterprise-scale apps.
Q3: Does React Native support offline apps?
Yes, with the help of libraries like Redux-Persist and SQLite.
Q4: What skills do developers need?
JavaScript, React, and some native development knowledge (Swift, Java, Kotlin).
Q5: Is React Native better than Flutter?
Both have pros and cons—React Native is easier for React/JS developers, while Flutter offers better UI flexibility.
Key Takeaways
-
React Native allows businesses to develop cost-effective, cross-platform mobile apps.
-
It provides near-native performance, faster development cycles, and a strong ecosystem.
-
Best suited for startups, SMEs, and enterprises across industries.
-
Despite minor limitations, its future looks strong with ongoing improvements.
Conclusion
React Native has established itself as a powerful framework for building modern, cross-platform mobile applications. By combining the ease of JavaScript with native component rendering, it offers the perfect balance between cost efficiency, scalability, and performance. Whether you’re a startup aiming for faster market entry or an enterprise looking to streamline development, React Native is an investment worth considering.