Introduction
In today’s hyper-connected digital world, data is the new oil — a powerful asset that drives innovation, strategy, and growth. Every second, billions of data points are generated from online transactions, social media, IoT devices, and business operations.
But raw data is meaningless unless it’s analyzed, interpreted, and used to make informed decisions. That’s where Big Data Analytics and Business Intelligence (BI) come into play.
Together, they empower organizations to uncover hidden trends, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
What Is Big Data Analytics?
Big Data Analytics is the process of examining large, complex datasets to discover hidden patterns, correlations, market trends, and customer preferences.
Unlike traditional data analysis, Big Data Analytics can handle massive volumes (terabytes or petabytes) of structured and unstructured data at lightning speed.
The 5 Vs of Big Data:
-
Volume – Massive amount of data generated daily
-
Velocity – Speed at which data is created and processed
-
Variety – Different formats (text, images, videos, logs, etc.)
-
Veracity – Accuracy and reliability of data
-
Value – Insights gained from analysis
By leveraging technologies like Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases, businesses can process and analyze enormous data efficiently.
What Is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business Intelligence is a technology-driven process for analyzing data and presenting actionable insights to help executives, managers, and employees make informed business decisions.
BI systems typically use dashboards, reports, and visualization tools like:
-
Power BI
-
Tableau
-
QlikView
-
Google Data Studio
BI tools collect data from multiple sources, integrate it, and display results through interactive visual dashboards, making insights accessible to everyone.
Big Data Analytics vs. Business Intelligence
| Aspect | Big Data Analytics | Business Intelligence (BI) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Predict future outcomes | Analyze past & present performance |
| Data Type | Structured + Unstructured | Mostly structured data |
| Tech Used | Hadoop, Spark, Machine Learning | Power BI, Tableau, SQL |
| Output | Predictive & prescriptive insights | Descriptive & diagnostic insights |
| Focus | Exploration & forecasting | Reporting & visualization |
In short, Big Data Analytics predicts what’s coming next, while Business Intelligence explains what’s happening now.
Together, they create a 360° view of the organization, enhancing data-driven strategies.
How Big Data and BI Work Together
When integrated, Big Data and BI enable organizations to:
-
Collect vast amounts of real-time data
-
Process and store it efficiently
-
Visualize complex patterns
-
Support strategic business decisions
Example:
A retail company can use Big Data Analytics to predict customer purchase trends and then use BI dashboards to visualize which products are performing best in real-time.
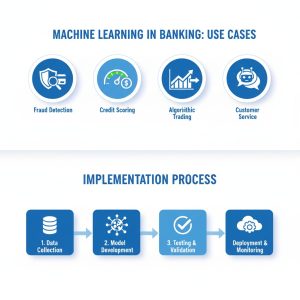
Key Components of Big Data and BI Ecosystem
1. Data Collection
Data is gathered from multiple sources — sensors, CRM systems, web logs, transactions, and social media.
2. Data Storage
Tools like Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), Amazon S3, or Google Cloud Storage store massive data volumes securely.
3. Data Processing
Frameworks such as Apache Spark and Flink process the data for analysis.
4. Data Analysis
Machine learning algorithms and statistical models identify patterns and trends.
5. Data Visualization
BI tools like Power BI or Tableau present the results in interactive dashboards and graphs.
Applications of Big Data and BI in Industries
1. Retail & E-Commerce
-
Personalized product recommendations
-
Dynamic pricing based on demand
-
Customer behavior tracking
Example:
Amazon uses predictive analytics to recommend products, improving sales and customer engagement.
2. Healthcare
-
Predictive diagnosis and treatment plans
-
Disease outbreak tracking
-
Patient data management
Example:
Hospitals use BI tools to monitor patient recovery and resource allocation.
3. Finance
-
Fraud detection using real-time analytics
-
Credit risk assessment
-
Algorithmic trading
Example:
Banks use Big Data to identify suspicious transactions within seconds.
4. Manufacturing
-
Predictive maintenance of equipment
-
Supply chain optimization
-
Quality control automation
5. Education
-
Performance analytics for students
-
Personalized learning paths
-
Data-driven decision-making in administration
Emerging Trends in Big Data and BI
-
Artificial Intelligence Integration:
Machine learning models now automate insights generation. -
Real-Time Analytics:
Instant decision-making with live data streaming. -
Data Democratization:
BI tools make analytics accessible to non-technical users. -
Augmented Analytics:
Combines AI and natural language processing (NLP) for smarter reports. -
Edge Analytics:
Data processing closer to the source for faster outcomes. -
Data Governance and Privacy:
Ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Benefits of Big Data Analytics and BI
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Informed Decision-Making | Data-backed strategic planning |
| Cost Optimization | Identify inefficiencies |
| Customer Insights | Understand preferences & behaviors |
| Predictive Capabilities | Anticipate future trends |
| Competitive Advantage | Gain market leadership |
| Operational Efficiency | Automate and streamline workflows |
Challenges in Big Data and BI Implementation
-
Data quality and integration issues
-
High storage and processing costs
-
Security and privacy risks
-
Shortage of skilled data professionals
-
Over-dependence on tools without clear strategy
However, with cloud-based solutions and AI-powered platforms, these challenges are becoming easier to overcome.
Conclusion
In the digital era, data is the foundation of success — but only when it’s analyzed effectively.
Big Data Analytics gives organizations predictive power, while Business Intelligence delivers clarity and visibility. Together, they transform information into strategic insight, fueling smarter, faster, and data-driven decision-making.
Companies embracing this synergy are not just surviving — they’re leading the future of business innovation.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between Big Data Analytics and Business Intelligence?
Big Data focuses on analyzing large datasets for predictive insights, while BI focuses on reporting and visualizing historical data.
2. Why are Big Data and BI important?
They help businesses make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and predict market trends.
3. What tools are used in Big Data Analytics?
Hadoop, Spark, Hive, and Flink are commonly used tools.
4. What are popular BI tools?
Power BI, Tableau, QlikView, and Google Data Studio are top BI tools.
5. What skills are needed for Big Data and BI?
Data analysis, SQL, Python, visualization tools, and knowledge of databases.