Introduction
Imagine a world where machines can think, learn, and perform tasks faster, safer, and more accurately than humans. That world isn’t science fiction — it’s happening right now, thanks to automation and robotics.
From factory floors to hospitals, logistics hubs to your kitchen, robots and automation systems are revolutionizing how we live and work. They don’t just improve productivity — they redefine what’s possible.
This blog explores how automation and robotics are driving innovation, reshaping industries, and creating a future where humans and machines collaborate seamlessly.
What Is Automation?
Automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention.
It’s about replacing repetitive, rule-based processes with smart systems that can work independently — reducing errors and improving speed.
Types of Automation
-
Fixed Automation:
Used in mass production lines (e.g., car manufacturing).-
High volume, low flexibility.
-
-
Programmable Automation:
Machines can be reprogrammed for different tasks.-
Used in batch production industries.
-
-
Flexible Automation:
Systems quickly adapt to new products or processes.-
Ideal for industries with frequent design changes.
-
-
Cognitive Automation (AI-driven):
Integrates machine learning and AI for decision-making and self-improvement.-
Used in customer service bots, predictive maintenance, and data analysis.
-
What Is Robotics?
Robotics is a branch of engineering that designs, builds, and operates robots — programmable machines that perform tasks automatically or semi-automatically.
Robots combine mechanical components, sensors, actuators, and AI to perform physical actions and make intelligent decisions.
Types of Robots
-
Industrial Robots: Perform assembly, welding, or packaging in factories.
-
Service Robots: Used in healthcare, hospitality, or home cleaning.
-
Autonomous Robots: Navigate environments independently (e.g., drones, self-driving vehicles).
-
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Work safely alongside humans.
-
Humanoid Robots: Mimic human gestures and expressions.
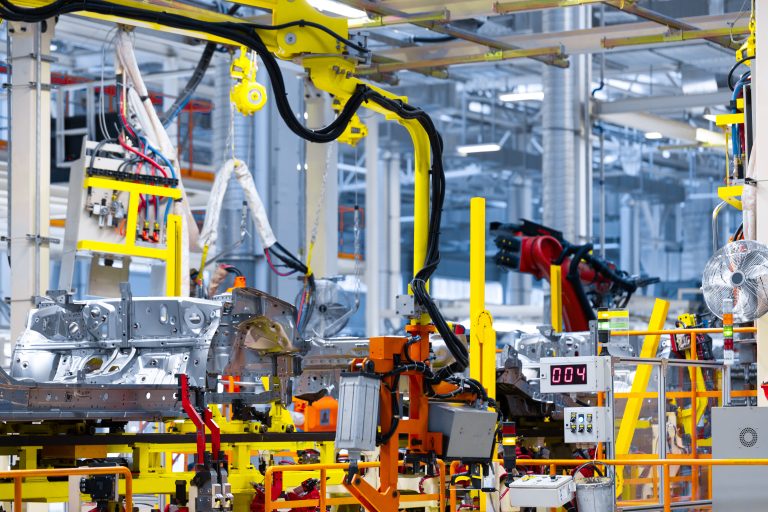
Automation and Robotics in Industry
Automation and robotics are the cornerstone of Industry 5.0, the new era of intelligent manufacturing focused on human-machine collaboration.
Manufacturing
-
Robots handle repetitive tasks like assembly, painting, and quality inspection.
-
AI-driven automation predicts equipment failures before they happen.
-
Cobots work side by side with human operators, enhancing safety and precision.
Example:
Companies like Tesla and BMW use robotic arms for car assembly, improving speed and accuracy.
Healthcare
Robots assist doctors in surgeries and automate hospital logistics.
-
Surgical robots perform precise operations with minimal invasion.
-
Delivery robots transport medicines and supplies.
-
AI automation manages patient data and diagnostics.
Example: The da Vinci Surgical System enables surgeons to perform complex procedures remotely with robotic precision.
Logistics and Supply Chain
Automation powers warehouse management and delivery systems.
-
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) move materials.
-
Drones deliver goods efficiently.
-
AI systems optimize inventory and routes.
Example:
Amazon’s fulfillment centers use robots to pick, pack, and ship millions of products daily.
Finance and Business
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive office tasks like data entry, report generation, and compliance checks.
-
Saves time and reduces human error.
-
Frees employees for higher-value work.
Example:
Banks use RPA to process loan approvals, detect fraud, and manage accounts.
Home and Daily Life
From vacuuming robots like Roomba to voice-controlled assistants like Alexa, automation is making homes smarter and lives easier.
Smart appliances can learn user habits and operate efficiently, saving energy and effort.
The Fusion of AI and Robotics
When Artificial Intelligence (AI) meets robotics, machines gain the ability to learn, adapt, and make decisions.
-
Computer vision enables robots to “see” and analyze surroundings.
-
Machine learning helps them improve performance over time.
-
Natural language processing allows them to interact with humans conversationally.
Example:
Boston Dynamics’ robots like “Atlas” and “Spot” combine AI and robotics to perform complex tasks like running, climbing, and opening doors.
Benefits of Automation and Robotics
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Efficiency | Machines can operate 24/7 without fatigue. |
| Precision & Consistency | Reduced errors and high-quality output. |
| Safety | Robots perform dangerous tasks, reducing workplace injuries. |
| Cost Savings | Long-term operational savings after initial setup. |
| Innovation | Enables new forms of production and services. |
Challenges in Automation and Robotics
Despite the advantages, challenges exist:
-
Job Displacement: Automation can replace routine tasks.
-
High Initial Investment: Robots and automation systems are costly to deploy.
-
Complex Integration: Requires skilled professionals and system compatibility.
-
Cybersecurity Risks: Connected robots can be vulnerable to hacking.
-
Ethical Dilemmas: Balancing human employment and machine efficiency.
However, the Industry 5.0 model focuses on collaboration, not replacement — using robots to assist humans, not eliminate them.
The Future of Automation and Robotics
The next decade will see automation evolve from mechanical efficiency to intelligent collaboration.
Key Future Trends:
-
Cobots in every industry
-
AI-driven autonomous systems
-
Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) business models
-
Sustainable automation for green manufacturing
-
Emotional and social robots for healthcare and education
Automation and robotics will become integral to every aspect of life — not just replacing humans but enhancing human potential.
Conclusion
Automation and robotics represent the next leap in human innovation — merging intelligence, precision, and reliability to reshape the future of work.
As we enter the Industry 5.0 era, the goal isn’t to remove humans from the equation but to empower them with intelligent machines that amplify creativity, safety, and productivity.
The future is not man versus machine — it’s man with machine, building a smarter, more efficient world together.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between automation and robotics?
Automation refers to using systems for automatic operations, while robotics involves machines physically performing tasks.
2. What industries use robotics the most?
Manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, and defense are leading sectors.
3. Will robots take over human jobs?
They’ll replace repetitive tasks but also create new roles in programming, maintenance, and AI system design.
4. What are collaborative robots (cobots)?
Cobots are robots designed to work safely alongside humans without barriers.
5. How is AI used in robotics?
AI helps robots learn, make decisions, and interact naturally with humans and their environment.