Introduction
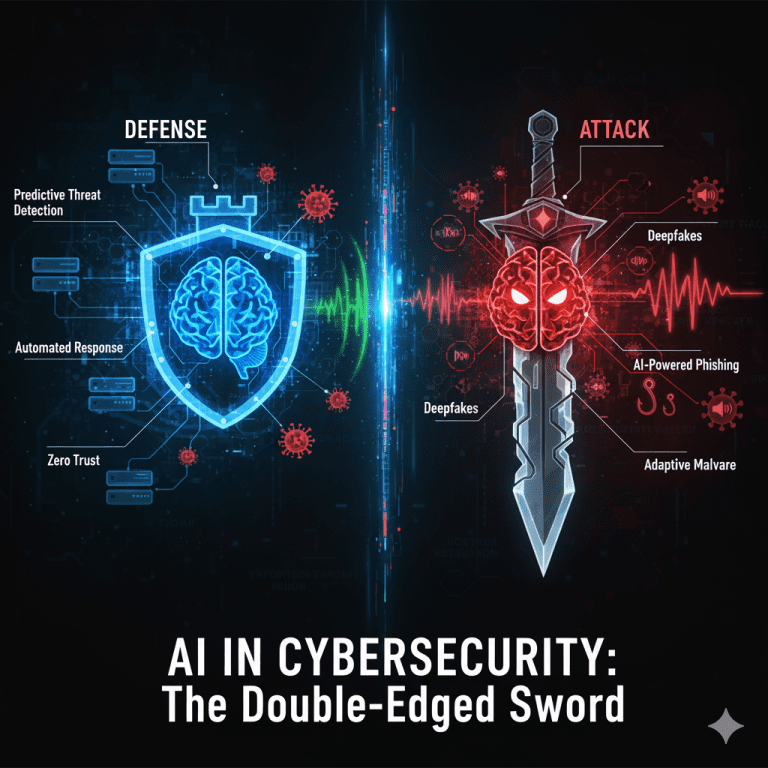
For decades, the world of cybersecurity has been a high-stakes cat-and-mouse game. Security professionals build a wall, and hackers find a way over it. But today, this game is being fundamentally transformed by a powerful new player: Artificial Intelligence. AI is not just another tool; it’s a revolutionary force acting as both the strongest shield and the most dangerous new weapon. This article explores the dual role of AI in Cybersecurity, breaking down how it’s creating unprecedented defenses while simultaneously arming attackers with terrifying new capabilities
The New Shield: AI as a Defensive Powerhouse
The primary advantage of AI in a defensive role is its ability to process and analyze data at a scale and speed no human team could ever hope to match. While a human analyst sleeps, an AI security model is monitoring billions of events, looking for the one tiny anomaly that signals an attack.
1. Predictive Threat Detection
Before AI, most security systems were reactive. They relied on “signatures”—the digital fingerprints of known malware. This meant a virus had to successfully attack someone first before it could be identified and blocked.
AI, specifically machine learning, is predictive. It learns the normal, baseline behavior of your network, your users, and your devices. It can then spot suspicious deviationsbefore a full-blown breach occurs.
This includes:
- Behavioral Analysis: Is a user account that normally works from 9-to-5 suddenly trying to access sensitive files at 3:00 AM from a different country? AI flags this instantly.
- Anomaly Detection: Does a “smart” device like a thermostat suddenly start trying to communicate with an unknown server? AI can see this as a potential IoT (Internet of Things) attack.
- Pattern Recognition: AI can analyze global threat feeds and identify new attack patterns as they emerge, proactively blocking them before they even reach your network.
2. Automated Incident Response
In a cyberattack, every second counts. A ransomware attack can encrypt an entire company’s files in minutes. AI doesn’t need to wait for approval; it can act in milliseconds. This is known as SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response).
Here’s a typical automated response scenario:
- Detect: An AI-powered sensor identifies a new, unknown program exhibiting ransomware-like behavior (e.g., rapidly encrypting files) on an employee’s laptop.
- Isolate: The AI immediately executes a predefined rule: it automatically disconnects that specific laptop from the company network, containing the threat.
- Investigate: The AI gathers all relevant data—what the program was, where it came from, what files it touched—and creates a report.
- Alert: It then sends an alert to a human security analyst, presenting the report and the action it took. The threat is neutralized before it could spread.
The Future: An AI vs. AI Battleground
This leads to an inevitable future: the front line of AI in Cybersecurity will be an AI-versus-AI battle. It will be a silent, high-speed war fought in milliseconds, with defensive AI models trying to detect and stop offensive AI-driven attacks.
In this new era, the old security model of “trust but verify” is dead. The new model, which AI is perfect for, is Zero Trust.
Zero Trust Architecture means you trust nothing and no one by default.
- It doesn’t matter if a login request comes from inside the office or outside; it must be verified.
- AI helps enforce this by continuously analyzing behavior. Just because you entered the right password doesn’t mean you are who you say you are. If your “logged-in” account suddenly starts acting suspiciously, the AI can force you to re-authenticate or block your access.
Conclusion
AI in Cybersecurity is a revolutionary, double-edged sword. It offers our most powerful hope for a secure digital future, capable of analyzing threats and responding at superhuman speeds. At the same time, it arms our adversaries with tools to create highly deceptive scams and intelligent malware.
The key takeaway is that we can’t ignore it. For businesses, investing in modern, AI-powered defensive tools is no longer an option—it’s a necessity for survival. For individuals, it requires a new level of vigilance. In this new world, adaptability is everything. The future of security will be defined by who has the smarter, faster, and more adaptable AI.
FAQ
Q1: What is AI in Cybersecurity? AI in Cybersecurity refers to the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect, predict, prevent, and respond to cyber threats. It moves beyond traditional, rule-based security by learning from data to identify new and unknown threats based on behavioral anomalies.
Q2: Can AI replace human cybersecurity professionals? No, AI is a tool to augment human professionals, not replace them. AI can handle the massive, high-speed data analysis, but it still lacks human intuition, creativity, and strategic decision-making. AI flags the problem and contains it; the human analyst investigates the “why” and “how” to build a stronger long-term strategy.
Q3: What is the biggest threat from AI in cyberattacks? Currently, the most accessible and dangerous threat is AI-powered social engineering, including deepfake audio and video. These attacks target the weakest link in any security system—human psychology—and are incredibly difficult to defend against with technology alone.
Q4: How can a small business afford AI-powered security? While developing a custom AI model is expensive, most AI-powered security is now sold “as-a-service.” Many modern antivirus, firewall, and email security providers (like Microsoft, Google, and CrowdStrike) have already integrated AI and machine learning into their standard products, making it accessible and affordable for businesses of all sizes.