Introduction
What do AI, cybersecurity, and the future of the internet (Web3) have in common? They all have critical problems with trust, security, and centralization. Blockchain technology is emerging as the key solution to all three. It’s the invisible architecture that provides the security for our data, the transparency for our transactions, and the ownership of our digital assets. Let’s dive into the technology ecosystem that blockchain is building right now.
What is Blockchain?
At its simplest, ablockchain is a secure, digital ledger that is shared among many computers in a network. Once a piece of information (a “block”) is added to the ledger, it is linked to the previous block using cryptography, creating a “chain.”
This structure makes itimmutable, meaning once data is recorded, it is extremely difficult to change or remove.
Core Components
- Decentralization: Instead of one person or company controlling the ledger (like a single bank), the ledger is copied and spread across many computers. This means no single entity has control, and there is no single point of failure.
- Cryptography: Every transaction is secured and verified using advanced math. This ensures that only the rightful owner can access their assets and that all records are authentic.
- Blocks: These are the “pages” of the ledger. Each block contains a batch of recent, verified transactions.
- Consensus Mechanism: This is the “rulebook” that the network follows to agree on which transactions are valid and can be added to the chain (e.g., Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake).
The Big Trends: Web3, DeFi, and NFTs
Blockchain is the foundational technology for several major trends:
- Web3: This is the idea of a new, decentralized internet.
- Web1 was the “read-only” internet (static websites).
- Web2 is the “read-write” internet we use today (social media, user-generated content), but it’s controlled by large tech companies.
- Web3 aims to be a “read-write-own” internet, where users control their own data and identity using blockchain.
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): This is an entire ecosystem of financial applications built on blockchain. It aims to recreate traditional financial systems (like lending, borrowing, and trading) without the need for intermediaries like banks. Users interact directly with smart contracts.
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): An NFT is a unique digital certificate of ownership for an asset (like a piece of digital art, a collectible, or even a real-world item). “Non-fungible” means it’s one-of-a-kind and cannot be replaced by another, unlike a dollar bill, which is fungible. This ownership is recorded and verifiable on the blockchain.
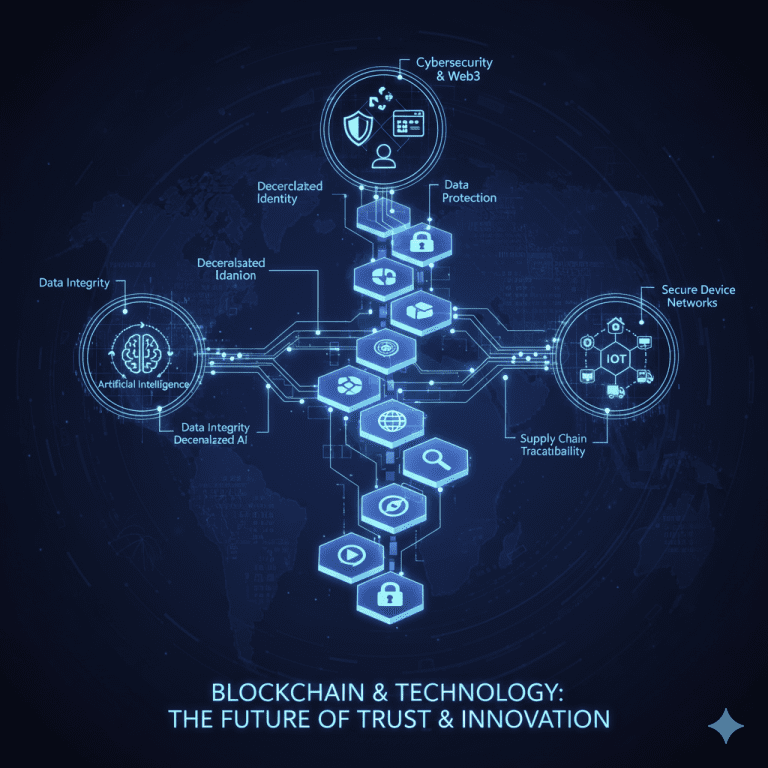
Blockchain’s Integration with Other Technologies
Blockchain doesn’t exist in a bubble. Its real power is unlocked when combined with other technologies.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Data Integrity: AI models are only as good as the data they’re trained on. Blockchain can provide an immutable, verifiable audit trail for AI training data, ensuring it hasn’t been tampered with and proving its origin.
- Decentralized AI: It enables “Federated Learning,” where an AI model can be trained across multiple devices without the users’ private data ever leaving their device. The blockchain is used to log and verify the model’s updates, protecting user privacy.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
- Security: IoT networks often have thousands of simple devices (like sensors) that are vulnerable to hacking. Blockchain can create a secure, decentralized network for these devices to communicate directly and verifiably, preventing a central server from being hacked.
- Traceability: For supply chains, an IoT sensor can log a package’s temperature and location to a blockchain at every step. This creates a tamper-proof record that all parties (the producer, the shipper, the customer) can trust.
3. Cybersecurity
- Decentralized Identity: Instead of relying on Google or Facebook to log in to websites, blockchain allows forSelf-Sovereign Identity (SSI). You would control your own digital identity, stored securely, and grant specific, temporary access to services that need to verify it.
- Mitigating Attacks: By decentralizing data storage, blockchain can help prevent large-scale data breaches. It also makes systems more resilient to Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, as there is no single central server to overwhelm
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain has evolved far beyond its origins in cryptocurrency. It is now the essential “trust layer” for the next generation of technology. By providing a decentralized, immutable, and transparent ledger, it solves the critical vulnerabilities in our current systems. It’s the thread that securely connects AI models to verifiable data, enables IoT devices to communicate without a central point of failure, and provides the very foundation for a user-owned internet in Web3, DeFi, and NFTs. As we move forward, it’s clear that blockchain isn’t just another technology in the stack; it’s the fundamental architecture the future is being built on.
FAQ
Q1: What is blockchain in the simplest terms?
Blockchain is a digital ledger, like a shared notebook, that is duplicated and spread across many computers. Once a transaction (a “block”) is added to this notebook, it’s cryptographically linked to the one before it, creating a “chain.” This structure makes the data immutable, meaning it’s nearly impossible to change or tamper with.
Q2: Isn’t blockchain just for Bitcoin and cryptocurrency?
No. While Bitcoin was the first major application, it’s just one use case. Blockchain is the underlying technology that enables cryptocurrencies, but its core value is in providing a secure and decentralized way to record any kind of data. It’s now being used in supply chains, healthcare, voting systems, cybersecurity, and more.
Q3: What’s the difference between Blockchain and Web3?
Think of blockchain as the tool and Web3 as the movement.
- Blockchain is the specific technology (a decentralized ledger).
- Web3 is the broader vision for a new, decentralized internet built using tools like blockchain, crypto, and decentralized networks. Web3’s goal is to shift control from large tech companies to individual users.
Q4: How does blockchain work with Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Blockchain can be seen as the “source of truth” for AI.
- Data Integrity: It provides a tamper-proof log of the data used to train an AI model, so you can verify its origin and quality.
- Privacy: It enables federated learning, where an AI can be trained on decentralized data sets without the raw data ever leaving the user’s control.
Q5: What is DeFi and how does it relate to blockchain?
DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance. It’s an entire ecosystem of financial applications (for lending, borrowing, trading) built on top of blockchain technology. It aims to recreate traditional financial systems but without the need for intermediaries like banks or brokerages.
Q6: Why do NFTs need a blockchain?
An NFT (Non-Fungible Token) is a digital certificate of ownership. The blockchain is used to publicly record and verify who owns that specific digital item. Without the blockchain, an NFT would just be a digital file that anyone could copy; the blockchain is what proves your unique, verifiable ownership.
Q7: How does blockchain make things more secure?
Blockchain’s security comes from its decentralized and cryptographic nature.
- Decentralized: Since the ledger is copied on thousands of computers, a hacker would have to attack a majority of the network (51%) simultaneously to change a record, which is practically impossible.
- Immutable: Every block is cryptographically linked to the one before it. Changing one block would break the entire chain, making any tampering immediately obvious.