Introduction
In the diverse and dynamic Java Virtual Machine (JVM) ecosystem, selecting the right programming language is a crucial decision for app developers. Among the premier choices, Kotlin and Scala stand out as powerful JVM languages offering unique features, developer experiences, and application potentials. Businesses and developers often ponder which language better suits their needs—from mobile app development to big data processing and enterprise applications.
This extensive blog examines the strengths and considerations of Kotlin and Scala, outlining key differences, industry use cases, community support, and ecosystem compatibility. With integrated insights on advanced technologies such as AI, blockchain, and predictive analytics from TechOTD AI Services, this guide aims to empower app developers and technology leaders to choose the ideal JVM language.
Background on JVM Languages
The Java Virtual Machine provides a platform-neutral environment enabling various languages to run on multiple operating systems seamlessly. JVM compatibility allows Kotlin, Scala, and Java to interoperate, sharing tooling, libraries, and runtime advantages. Understanding the design philosophy and ecosystem dynamics surrounding Kotlin and Scala is essential for informed decision-making.
-
Learn about AI and JVM language applications at TechOTD AI Blog.
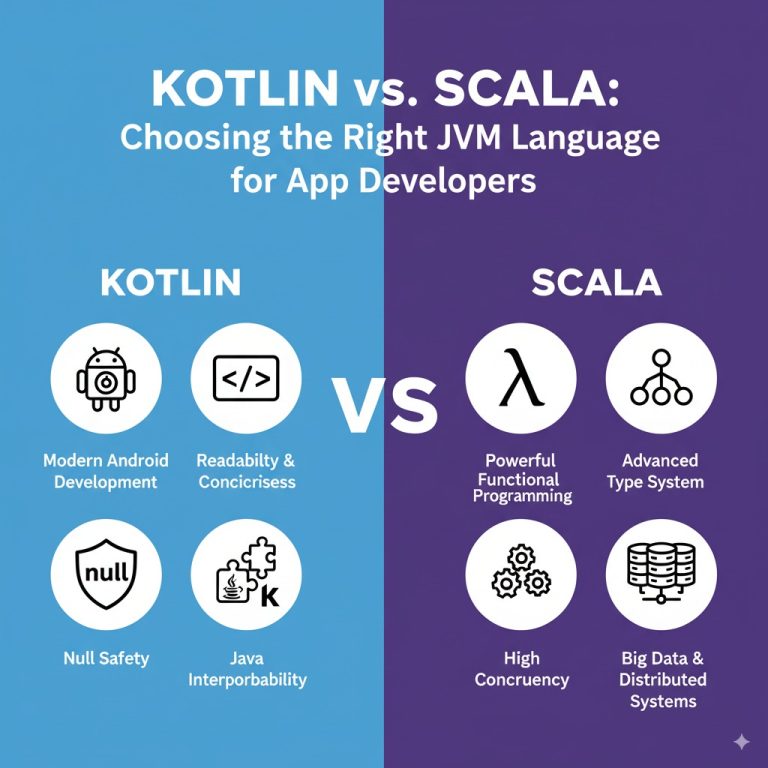
Kotlin: Modern, Pragmatic, and Android-Focused
Language Overview
Developed by JetBrains and officially endorsed by Google for Android, Kotlin is a statically typed language designed to be concise, safe, and fully interoperable with Java.
-
Focus on simplicity and readability.
-
Supports functional programming features alongside object-oriented paradigms.
-
Null safety and coroutines for asynchronous programming improve developer safety and productivity.
Strengths of Kotlin
-
Android Excellence: Native support and extensive tooling make Kotlin the preferred choice for Android app development TechOTD Mobile Apps.
-
Concise Syntax: Less boilerplate code than Java, improving maintainability.
-
Strong Tooling Integration: Exceptional support in IntelliJ IDEA, Android Studio, and Gradle.
-
Coroutines: Efficient async programming for responsive UI and backend services.
-
Safety Features: Null safety reduces runtime exceptions.
Ideal Use Cases
-
Android application development.
-
Backend services using frameworks like Ktor or Spring Boot.
-
Multiplatform projects targeting iOS, JVM, JavaScript with Kotlin Multiplatform.
-
Data science and scripting through integration with JVM tools.
Scala: Powerful, Expressive, and Big Data-Ready
Language Overview
Scala was created to enrich Java with concise syntax, powerful functional programming capabilities, and advanced type system features, aiming for seamless JVM interoperability.
-
Blends object-oriented and functional programming paradigms.
-
Supports advanced features such as pattern matching, implicits, and macros.
-
Strong presence in big data, distributed computing, and complex backend systems.
Strengths of Scala
-
Functional Programming: Modern functional constructs offer flexibility and safety.
-
Rich Type System: Enables precise modeling of domain logic.
-
Big Data Ecosystem: Widely adopted with Apache Spark, Kafka, and Akka for analytics and real-time processing.
-
Conciseness and Expressiveness: Reduces code verbosity with powerful abstractions.
-
Compatibility: Runs on JVM with Java interoperability.
Ideal Use Cases
-
Big data and analytics applications.
-
Complex backend systems requiring concurrency and scalability.
-
Distributed systems development.
-
Enterprise applications needing expressive domain modeling.
Comparing Kotlin and Scala: A Feature Breakdown
| Aspect | Kotlin | Scala |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Curve | Gentler, easier for Java developers | Steeper, requires functional paradigm understanding |
| Syntax Complexity | Simpler, concise | More complex, expressive |
| Performance | Comparable to Java | Comparable, can optimize with advanced features |
| Functional Programming | Supported, but limited | Extensive support |
| Android Support | Primary JVM language for Android | Limited support in Android ecosystem |
| Tooling | Fantastic IDE integration | Good but occasionally slower builds |
| Community and Ecosystem | Rapidly growing, strong in mobile/devops | Mature, especially in big data and backend |
| Deployment Size | Smaller, better suited for mobile | Larger JVM footprints |
Ecosystem and Community Support
-
Kotlin enjoys strong backing from JetBrains and Google, ensuring ongoing investments and modern tooling TechOTD Blog.
-
Scala has an established base with academic and enterprise support, particularly within big data frameworks like Apache Spark.
-
Both languages benefit from seamless Java interoperability, enabling gradual adoption and integration.
Integration with AI, Blockchain, and Predictive Analytics
-
Kotlin, with its modern syntax and multiplatform capabilities, is increasingly used in AI-driven mobile apps and blockchain projects TechOTD AI Services.
-
Scala’s functional programming and big data compatibility make it ideal for building predictive analytics pipelines and blockchain data processing TechOTD Blockchain Integration.
-
Explore predictive analytics development techniques leveraging JVM languages at TechOTD Predictive Analytics.
Implementation Best Practices
Planning and Skill Assessment
Evaluate team expertise and project requirements before choosing.
Prototype Development
Build small proof-of-concept projects to validate feasibility.
Code Quality and Maintenance
Prioritize clean, readable, and maintainable code; Kotlin’s simpler syntax may aid this.
Testing and CI/CD
Leverage JVM testing frameworks and continuous integration for robust delivery.
Community Engagement
Participate in forums and learn from open-source projects to accelerate learning and troubleshooting.
Future Trends in JVM Language Development
-
Kotlin is expanding with multiplatform capabilities supporting iOS, JS, and native apps.
-
Scala continues evolving with Scala 3, simplifying syntax and enhancing language consistency.
-
Both languages are incorporating improved tooling for AI, blockchain, and cloud-native applications.
-
Growing adoption of JVM languages in government, finance, healthcare, and IoT.
Conclusion
Choosing between Kotlin and Scala depends on project goals, developer expertise, and application needs. Kotlin shines in mobile-first, agile, and straightforward backend apps, while Scala excels in complex, data-intensive, and functional programming domains. Both contribute significantly to modern JVM ecosystems and enable powerful, scalable applications.